Oceanologia No. 38 (1) / 96
Contents
Papers
Communications
Dissertations
Papers
Piotr Kowalczuk, Sławomir Kaczmarek
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Analysis of temporal and spatial variability of "yellow substance"
absorption in the southern Baltic
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 3-32
Keywords: Inherent optical properties; Absorption; Yellow substance; Southern Baltic
Manuscript received September 25, 1995, in final form January 15, 1996.
Abstract
The value of the yellow substance absorption
coefficient in the visible-light spectrum is
a very important characteristic used in the optical
classification of seawaters. The absorption of yellow
substance also needs to be included in algorithms for the
remote detection of optically-active seawater constituents.
This paper presents the results of an analysis of yellow substance
absorption coefficient data, ay ,
collected during 11 cruises in the southern Baltic.
The statistical distribution of the value of ay(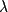 = 400 nm)
and the value of the yellow substance absorption
spectrum slope coefficient are analysed. The range of
spatial and temporal variability of these parameters is discussed,
and the auto-correlation matrix of the absorption coefficient
measured at different wavelengths is analysed.
Particular attention is given to selected wavelengths,
essential in evaluating the influence of changes
of ay on the spectral reflectance.
= 400 nm)
and the value of the yellow substance absorption
spectrum slope coefficient are analysed. The range of
spatial and temporal variability of these parameters is discussed,
and the auto-correlation matrix of the absorption coefficient
measured at different wavelengths is analysed.
Particular attention is given to selected wavelengths,
essential in evaluating the influence of changes
of ay on the spectral reflectance.
Waldemar Grzybowski
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Selected properties of different molecular size fractions of humic
substances isolated from surface Baltic water in the Gdańsk Deep area
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 33-47
Keywords: Humic substances; Baltic water; Heavy metals; Complexation
Manuscript received May 10, 1995, in final form October 9, 1995.
Abstract
Humic substances were isolated from
surface Baltic water in the Gdańsk Deep area and
fractionated by ultrafiltration on membrane filters
of pore sizes 1000, 5000 and 10 000 Daltons.
97% of the material obtained was smaller than 10 000 D.
The fractions were characterised by UV-VIS and IR spectroscopy,
and analysed for elemental composition and functional group
concentration. The nitrogen and phenolic hydroxyl group concentrations
confirmed the autochthonous origin of the fractions. The aromaticity
of the molecules was found to increase with molecular size,
and the greatest saturation of aromatic rings with carboxyl
groups was found in the fraction smaller than 1000 D.
Complexation capacity was not directly connected with
molecular size. All the fractions possessed a larger capacity
for lead than cadmium, the complexation of the latter
being detected only in the < 1000 D fraction.
Marian Stoń
Institute of Physics , Pedagogical University, Słupsk
Determination of the structure of an oil-seawater emulsion from measurements
of light attenuation
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 49-59
Keywords: Light attenuation; Oil-water emulsions; Structure of polydispersive systems
Manuscript received May 30, 1995, in final form November 22, 1995.
Abstract
The effect of the statistical distribution parameters
of nonabsorbing particles on the transparency of
polydispersive systems is described. A method of inverting
the transmission spectra into the size distribution of
scattering particles is presented. It was tested on an
emulsion of Baltic crude oil in artificial Baltic seawater
and was found to provide useful information on the structure
of emulsions containing particles < 1 µm in size.
Joanna Szczucka, Zygmunt Klusek
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Migration patterns of acoustic scatterers in the southern Baltic Sea
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 61-79
Keywords: Marine acoustics; Scattering layers; Diurnal migration; Baltic Sea
Manuscript received November 16, 1995, in final form January 16, 1996.
Abstract
Echosounding records made at a fixed point of
the Gdańsk Deep at different seasons
(spring, summer, autumn, winter) were used to determine
the seasonal and diurnal migration patterns of plankton
layers in connection with thermohaline conditions.
Apart from some seasonal differences, a major,
common pattern of vertical migrations at sunrise and
sunset was observed. The width and scattering strength of
the layer formed at night in the water column depends
on the temperature gradient in the thermocline. The differences
in the total energy backscattered by biological aggregations
at different frequencies allow inferences to be drawn
about the dominant size of scatterers.
Jan Piechura, Waldemar Walczowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Interannual variability in the hydrophysical fields of
the Norwegian-Barents Seas confluence zone
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 81-98
Keywords: Arctic Seas; Hydrography; Variability
Manuscript received September 14, 1995, in final form October 31, 1995.
Abstract
Every summer since 1987 (except 1990), the Institute of
Oceanology has conducted oceanographic research in the area
between Norway and Spitsbergen, and between
12 and 17oE from the board of r/v "Oceania".
The data collected show quite substantial,
interannual variations in physical properties and transport.
In the north-east corner of the area investigated (close to Storfjord)
surface-water temperatures differed by > 6oC (2.6oC
in summer 1993 and 8.8oC in summer 1992) and salinity by > 1.5 PSU.
The depth of the thermocline and temperature gradients fluctuated,
as did the depth of the maximum salinity layer.
Water transport across the 15oE meridian in the
upper 1000 m layer calculated by geostrophic methods varied from
2.6 to 8.9 Sv eastwards and from 1.1 Sv to 5.1 Sv westwards.
The largest variations were observed in the surface
waters and in the north-eastern and south-eastern parts of the
confluence zone, i.e. in the areas most strongly influenced
by Barents Sea waters. In the areas occupied by Norwegian-Atlantic
waters and in deeper layers, conditions were much more stable.
Stefan Cebulak
Faculty of Earth Sciences, Scientific-Educational Laboratory, Silesian
University, Sosnowiec
Marcin Pliński
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
A new application of oxyreactive thermal analysis in marine
algological studies
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 99-112
Keywords: Algae; Methodology; Oxyreactive thermal analysis;
Taxonomical differentiation
Manuscript received May 16, 1995, in final form October 12, 1995.
Abstract
This is a preliminary study of the application of oxyreactive
thermal analysis in algological investigations.
Several species of Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta and Zostera marina
taken from different stations off the southern Baltic coast have
been studied. It is pointed out that oxyreactive thermal analysis
can be used for taxonomical investigations in order to establish
the systematic membership of certain species of algae based on
fragments of thallus. This method can also be applied in order to
establish environmental specificity by differentiating the
chemical composition of certain species. It is also suitable for
assessing biochemical differentiation among the various parts of the thallus.
Monika Normant, Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
The biochemical composition of Saduria (Mesidotea) entomon
(Isopoda) from the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Baltic)
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 113-126
Keywords: Crustacea; Biochemical composition; Saduria entomon
Manuscript received October 6, 1995, in final form November 30, 1995.
Abstract
The biochemical composition of specimens of S. entomon
from the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Baltic) has been investigated.
The average values found, expressed as a percentage of dry weight,
are as follows: 28.8% proteins, 6.7% lipids, 8.0%
carbohydrates and 28.0% ash. Seasonal variation in the
biochemical composition of S. entomon was observed
during the study period.
The differences in protein, lipid, carbohydrate and ash content
between males and females were not statistically significant
(p > 0.05). The relatively small average contents of individual
components compared to those in other crustaceans from the
Gulf of Gdańsk may have resulted from the broad food
preferences of S. entomon, ensuring its access to nutrients
throughout the year.
Urszula Janas, Anna Szaniawska
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
The influence of hydrogen sulphide on macrofaunal
biodiversity in the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 127-142
Keywords: Hydrogen sulphide; Sediment; Zoobenthos
Manuscript received October 8, 1995, in final form November 11, 1995.
Abstract
Investigations into the occurrence and concentrations of hydrogen sulphide
in sediments of the Gulf of Gdańsk were carried out
in September 1994. It was found that the concentration of H2S increased with basin and sediment depths.
The highest concentration (1244 µmol dm-3) was recorded in the 4-8 cm sediment layer at the deepest of the stations
investigated (station 14; 82 m depth). The studies demonstrated
that numerous species belonging to the macrozoobenthos are
exposed to H2S concentrations from several to several
hundred µmol dm-3. These are both deep-water species - Macoma balthica, Harmothoe sarsi, Saduria
entomon, Pontoporeia femorata - and shallow-water
species - Corophium volutator, Mya arenaria.
High concentrations of hydrogen sulphide, i.e.
> 1000 µmol dm-3, caused the number of
different macrozoobenthos species to decrease, even
though abundance and biomass levels remain high.
The studies indicated that the presence of hydrogen
sulphide is best tolerated by two species - Macoma balthica and Harmothoe sarsi.
Communications
Zygmunt Klusek, Krzysztof Poraziński
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The diurnal migration pattern of plankton in the Gulf of
Gdańsk during storm-induced onshore - offshore bottomwater transport
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 143-149
Keywords: Marine acoustics; Hydrology; Gulf of Gdańsk
Abstract
This paper describes a front carrying warm and salt water,
changing the depth of the thermocline and halocline in the
Gulf of Gdańsk, measured by in situ (CTD) and
remote sensing (acoustic sounding) methods.
Dissertations
Jarosław Tęgowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Characteristics of backscattered ultrasonic signals from the floor
of the southern Baltic
Oceanologia 1996, no. 38 (1), pp. 151-152
Ph. D. thesis in marine physics supervised by Associate Professor Zygmunt Klusek.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page
 Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
Sabina Szczykowska <sabina@iopan.gda.pl>
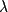 = 400 nm)
and the value of the yellow substance absorption
spectrum slope coefficient are analysed. The range of
spatial and temporal variability of these parameters is discussed,
and the auto-correlation matrix of the absorption coefficient
measured at different wavelengths is analysed.
Particular attention is given to selected wavelengths,
essential in evaluating the influence of changes
of ay on the spectral reflectance.
= 400 nm)
and the value of the yellow substance absorption
spectrum slope coefficient are analysed. The range of
spatial and temporal variability of these parameters is discussed,
and the auto-correlation matrix of the absorption coefficient
measured at different wavelengths is analysed.
Particular attention is given to selected wavelengths,
essential in evaluating the influence of changes
of ay on the spectral reflectance.
 Back to IO PAS Home Page
Back to IO PAS Home Page