Oceanologia No. 39 (3) / 97
Contents
Papers
- Tymon Zieliński: Aerosol masses and mass gradients in the marine boundary layer
over the breaker zone
- Maria Chomka, Tomasz Petelski:
Modelling the sea aerosol emission in the coastal zone
- Wiesław Kiciński:
A statistical model for classifying ambient noise in the sea
- Zygmunt Klusek, Joanna Szczucka, Stanisław Rudowski:
An attempt to use a broadband acoustic signal for determining the
dimensions of Baltic fish
- Grażyna Kowalewska, Joanna Konat, Brygida Wawrzyniak-Wydrowska:
Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the sediments of the Oder Estuary
(Szczecin Lagoon) before the flood of 1997
- Grażyna Kowalewska, Joanna Konat:
The role of phytoplankton in the transport and distribution of
polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the southern Baltic environment
- Bharat K. Ramavat, Ksenia Pazdro, Alicja Kosakowska, Janusz Pempkowiak:
Fatty acid content in seaweeds from the Baltic Sea and the Indian Ocean
- Agnieszka Beszczynska-Moller, Jan Marcin Węsławski, Waldemar
Walczowski, Marek Zajaczkowski: Estimation of glacial meltwater discharge into Svalbard coastal waters
- Ashraful Mohammed Haque, Maria Szymelfenig, Jan Marcin Węsławski:
Spatial and seasonal changes in the sandy littoral zoobenthos of
the Gulf of Gdańsk
- Agata Rychter:
Effects of anoxia on the behaviour, haemolymph lactate
and glycogen concentrations in the mud crab
Rhithropanopeus harrisii ssp. tridentatus (Maitland)
(Crustacea: Decapoda)
Dissertations
Papers
Tymon Zieliński
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Aerosol masses and mass gradients in the marine boundary layer
over the breaker zone
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 201-219
Keywords: Aerosol concentrations; Aerosol mass; Mass gradients; Wind;
Lidar; Baltic Sea
Manuscript received July 7, 1997, in final form August 7, 1997.
This research is part of the Polish State Committee for Scientific
Research, grant No. 6 P04E03611.
Abstract
The aerosol size distribution function and aerosol
concentration in the marine boundary layer depends strongly on
wind speed, direction and duration. Measurements were therefore
carried out in various seasons of the year, with all the above
factors and different types of sea bottoms being taken into
consideration. By employing the size distribution function and
concentrations of aerosol particles, which were determined in
the coastal zones of the southern Baltic Sea by means of the
lidar method, the aerosol masses and their gradients in the
marine boundary layer were calculated. It was found that for
onshore winds the concentrations and gradients were
substantially lower when compared with those for winds blowing
off the land.
Maria Chomka, Tomasz Petelski
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Modelling the sea aerosol emission in the coastal zone
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 211-225
Keywords: Aerosol; Flux; Coastal zone
Manuscript received June 16, 1997, in final form July 18, 1997.
Abstract
A model of aerosol emission from the coastal zone is presented.
Based on the equation describing wind-wave energy dissipation in the
coastal zone of the sea, it enables the aerosol emission from
any coastal zone to be calculated provided the parameters of
wave motion in a deep sea and the bathymetry are known.
The aerosol emissions for a real bottom profile (the coastal
station at Lubiatowo, southern Baltic Sea) are given.
The effect of the sea bottom profile on aerosol emission is
discussed on the basis of numerous implementations of the model.
The logarithmic relationship between the total aerosol
emission flux from the coastal zone and the tangent of the
bottom slope is demonstrated, and the total aerosol
emission from a coastal zone with a smooth sea-bed is
compared with that from a coastal zone with a rough bed.
The aerosol emission flux is independent of wave size in
deep water at short distances from the shore.
Wiesław Kiciński
The Polish Naval Academy, Gdynia
A statistical model for classifying ambient noise in the sea
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 227-235
Keywords: Ambient noise; Sea-state classification
Manuscript received January 14, 1997, in final form June 18, 1997.
This work was supported by grant No. 8T11B02710 from the
Polish State Committee for Scientific Research. Parts of this paper were presented at the conference on Sea Surface Sound,
Southampton, U. K., 1997.
Abstract
The article discusses the results of a multidimensional approach to the
investigation of ambient noise. The methodology for the characterisation of
ambient noise is discussed and the results of its
application in the classification of sea-states are considered.
The main problem in classifying sea-state using multidimensional statistical
methods is to determine the distinctive features of ambient noise.
The data were processed in the time and frequency domains.
The autoregressive model of ambient noise was applied in the time domain,
and its coefficients were used as
discriminatory terms for classifying and identifying sea-states. The third
octave spectrum was used to extract the distinctive features of ambient
noise in the frequency domain. The data were analysed in the 2-128 Hz
frequency band.
The data sets were processed using Fisher's linear functions.
The order of the autoregressive model and the third octave frequencies
were found to
classify the sea state. The distinctive features of ambient noise were
determined with
respect to time and frequency. Finally, the parameters of two statistical
models were used to classify sea states.
Zygmunt Klusek, Joanna Szczucka
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Stanisław Rudowski
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
An attempt to use a broadband acoustic signal for determining the
dimensions of Baltic fish
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 237-253
Keywords: Marine acoustics; Resonant scattering by swimbladders;
Broadband signals
Manuscript received July 8, 1997, in final form August 18, 1997.
This research was financially supported by the Polish State Committee for
Scientific Research, grant No. 6 P202 022 07.
Abstract
The resonant scattering of sound by fish swimbladders
is described. Broadband acoustic signals scattered by fish schools
in shallow water were analysed in order to find the resonant
frequencies of fish swimbladders and to determine the fish
length. Different spectral techniques were applied in order to
discern the resonance peaks in the scattered signal spectrum.
Grażyna
Kowalewska, Joanna Konat
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Brygida Wawrzyniak-Wydrowska
Department of Biological Oceanography, Szczecin University, Szczecin
Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the sediments of the Oder Estuary (Szczecin Lagoon) before the flood of 1997
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 255-266
Keywords: PAHs; Sediments; Pigments; Oder Estuary (Szczecin Lagoon);
Baltic Sea; HPLC
Manuscript received July 31, 1997, in final form August 18, 1997.
Abstract
Concentrations of 12 unsubstituted PAHs were
determined in sediments of the Oder Estuary (Szczecin
Lagoon), an exceptional aquatic basin on the Baltic coast,
collected in 1996, i.e. before the flood of 1997.
Four-ring PAHs (fluoranthene and pyrene) were the most
abundant, six-ring PAHs the least abundant group of PAHs,
as is the case in the coastal southern Baltic sediments.
The PAH concentration levels were higher than those recorded in the
southern Baltic Sea (av. Σ PAHs - 1830 ng g -1, benzo(a)pyrene
(B(a)P) - 98 ng g -1), and higher in samples collected in August
(av. Σ PAHs - 4960 ng g -1, B(a)P - 319 ng g -1) than in October
(av. Σ PAHs - 4581 ng g -1, B(a)P - 281 ng g -1). This result
is consistent with the fact that the coastal area is mainly responsible for
PAH pollution of the Baltic Sea, and that unsubstituted PAHs are of
pyrogenic origin. Their concentration should therefore decrease after
summer, since their residence time in the Oder Estuary is very short. PAHs
are scavenged from the water column by phytoplankton, mainly by
living phytoplankton cells. This conclusion confirms the previous results
obtained for sediments from the southern Baltic Sea. The sorption of
unsubstituted PAHs by phytoplankton cells varies, depending not only on the
concentration and physico-chemical properties of the PAH in question but
also on the symmetry of its molecule.
Grażyna Kowalewska, Joanna Konat
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
The role of phytoplankton in the transport and distribution of
polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the southern Baltic environment
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 267-277
Keywords: Phytoplankton; PAHs; Pigments; Baltic Sea; Oder Estuary
(Szczecin Lagoon)
Manuscript received June 26, 1997, in final form September 5, 1997.
Abstract
PAHs (12 compounds from phenanthrene to benzo(g,h,i)perylene)
were determined in plankton samples collected
from the southern Baltic Sea and the Oder Estuary (Szczecin Lagoon) in 1996.
The maximum Σ PAH (sum of 12 PAHs) concentrations were 16 000
ng g -1, i.e. values about twice as high as the maximum levels in
sediments of the southern Baltic and the Oder Estuary. PAHs
are selectively sorbed from water by phytoplankton, depending not
only on their physico-chemical properties like solubility,
but also on their molecular structure. The results obtained
indicate that phytoplankton plays a decisive role in the transport
and distribution of PAHs in the southern Baltic environment.
Bharat K. Ramavat
Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute, Bhavanagar, India
Ksenia Pazdro, Alicja Kosakowska, Janusz Pempkowiak
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Fatty acid content in seaweeds from the Baltic Sea and the Indian Ocean
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 279-287
Keywords: Fatty acid content; Composition; Seaweeds; Indian Ocean; Baltic Sea
Manuscript received June 26, 1997, in final form July 21, 1997.
Abstract
Two species of red marine macroalgae (Rhodophyceae) from the Indian Ocean,
two species of brown marine macroalgae (Phaeophyceae) and one species of
green marine macroalgae (Chlorophyceae) from the Baltic Sea were examined
for fatty acid composition and content. Fatty acids were quantified by means
of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of their coumaryl esters.
The total fatty acid content ranged from 220 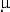 g g-1 d.w. in red
algae Grateloupia indica to 12 600
g g-1 d.w. in red
algae Grateloupia indica to 12 600 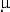 g g-1 d.w. in red algae
Acantophora spicifera. The proportions of particular fatty acids
varied considerably in these species. Palmitic acid (16:0) was dominant in
all the species investigated (58-68%) except for G. indica, which
contained only 11% of this acid. The Baltic green algae Enteromorpha
clathrata was characterised by a high amount of linolenic acid (16.7%),
whereas the red macroalgae from the Indian Ocean A. spicifera contained
large amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (13%) and oleic acid (11%).
g g-1 d.w. in red algae
Acantophora spicifera. The proportions of particular fatty acids
varied considerably in these species. Palmitic acid (16:0) was dominant in
all the species investigated (58-68%) except for G. indica, which
contained only 11% of this acid. The Baltic green algae Enteromorpha
clathrata was characterised by a high amount of linolenic acid (16.7%),
whereas the red macroalgae from the Indian Ocean A. spicifera contained
large amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (13%) and oleic acid (11%).
Agnieszka Beszczyńska-Möller, Jan Marcin Węsławski, Waldemar
Walczowski, Marek Zajączkowski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Estimation of glacial meltwater discharge into Svalbard coastal waters
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 289-298
Keywords: Arctic coastal waters; Freshwater budget; Fjords; Hydrology
Manuscript received June 16, 1997, in final form August 29, 1997.
This paper was sponsored by statutory research, subject 4.1--4.3,
carried out at the Institute of Oceanology PAS in Sopot.
Financial support was also received from the Polish State Committee
for Scientific
Research, grant supervised by Professor Jacek Jania
of the University of Silesia, Sosnowiec. Data were collected within
the BIODAFF framework programme.
Abstract
During the summer expeditions of r/v 'Oceania' in 1995-1996,
oceanographic investigations comprising CTD profiling and suspension
measurements were conducted in Svalbard fjords and shelf waters.
The freshwater volume was estimated independently from the salinity
drop as compared with the assumed background salinity and from
the distribution of mineral suspension density in surface
waters. Preliminary calculations of the instantaneous
freshwater volume based on the distribution of suspended
matter (at depths of < 150 m) yielded a figure of 80 km3 in
Svalbard coastal waters in summer. Values for Hornsund
and Kongsfjord ranged from 0.4 to 0.7 km3 of freshwater
at the height of summer. This corresponds well with
glaciological estimations, which give an annual discharge
of 14.6 to 27.5 km3 of freshwater for Svalbard. The glacial
discharge is estimated to make up some 42% of the
freshwater budget of Svalbard shelf waters, the remainder
being derived from Barents Sea Arctic waters of reduced
salinity.
Ashraful Mohammed Haque, Jan Marcin Węsławski
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Maria Szymelfenig
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Spatial and seasonal changes in the sandy littoral zoobenthos of
the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 299-324
Keywords: Baltic littoral; Benthos
Manuscript received June 30, 1997, in final form September 15, 1997.
Abstract
The meiobenthos and macrobenthos of the sandy littoral (about
1 m depth) were studied monthly in 1993 at three localities on
the Gulf of Gdańsk. The average abundance ranged from 0 to
15 159 indiv. m -2 for macrofauna and from 101 to 4193
indiv. 10-1 cm-2 for meiofauna. The respective
average biomass ranged from 0 to 51.5 g m-2 and from 0.05
to 2.45 mg 10-1 cm-2. The zoobenthos biomass
and abundance show two distinct seasonal peaks in May and late
September. The macrofauna was dominated by polychaetes
(Nereis diversicolor),
the meiofauna by Nematoda and Oligochaeta. Twenty-two
macrobenthos taxa were found in the samples examined, which
makes the littoral of the Gulf of Gdańsk highly diverse when compared to
the open Baltic coast. The meiobenthos consisted of similar higher
taxa known from other localities of the temperate zone.
Agata Rychter
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Effects of anoxia on the behaviour, haemolymph lactate
and glycogen concentrations in the mud crab
Rhithropanopeus harrisii ssp. tridentatus (Maitland)
(Crustacea: Decapoda)
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (3), pp. 325-335
Keywords: Crustacean; Crab, Rhithropanopeus harrisii
trinentatus; Anoxia; Behaviour; Metabolism
Manuscript received July 9, 1997, in final form September 16, 1997.
Abstract
The ability to accumulate lactate as result of laboratory exposure to anoxia was determined in the mud crab
Rhithropanopeus harrisii tridentatus. Haemolyph lactate levels rose from 0.232 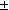 0.13
0.13 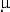 mol ml-1 to
25.337
mol ml-1 to
25.337 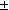 1.6
1.6 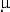 mol ml-1 during 32 h of anoxia.
High haemolymph lactate levels resulting from anoxia were associated with a
number of behavioural responses. The response of
R. harrisii tridentatus to very low levels of oxygen < 2 Torr
was relatively slow (LT 50= 24.3 h). Glycogen was found in
normoxic concentrations of 15.21
mol ml-1 during 32 h of anoxia.
High haemolymph lactate levels resulting from anoxia were associated with a
number of behavioural responses. The response of
R. harrisii tridentatus to very low levels of oxygen < 2 Torr
was relatively slow (LT 50= 24.3 h). Glycogen was found in
normoxic concentrations of 15.21 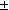 4.68
4.68 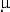 mol g-1 d.w.
These decreased after 6 h exposure to anoxia. The results are
discussed in relation to the metabolic requirements for
the survival of other crustaceans under low oxygen
conditions.
mol g-1 d.w.
These decreased after 6 h exposure to anoxia. The results are
discussed in relation to the metabolic requirements for
the survival of other crustaceans under low oxygen
conditions.
Dissertations
Ashraful Mohammed Haque
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Zoobenthos of the sandy littoral of the Gulf of Gdańsk
(review by J. M. Węsławski)
Oceanologia
1997, no. 39 (1), pp. 337-337
Ph. D. thesis in biological oceanography supervised by Associate Professor Jan Marcin Węsławski.
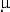 g g-1 d.w. in red
algae Grateloupia indica to 12 600
g g-1 d.w. in red
algae Grateloupia indica to 12 600 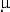 g g-1 d.w. in red algae
Acantophora spicifera. The proportions of particular fatty acids
varied considerably in these species. Palmitic acid (16:0) was dominant in
all the species investigated (58-68%) except for G. indica, which
contained only 11% of this acid. The Baltic green algae Enteromorpha
clathrata was characterised by a high amount of linolenic acid (16.7%),
whereas the red macroalgae from the Indian Ocean A. spicifera contained
large amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (13%) and oleic acid (11%).
g g-1 d.w. in red algae
Acantophora spicifera. The proportions of particular fatty acids
varied considerably in these species. Palmitic acid (16:0) was dominant in
all the species investigated (58-68%) except for G. indica, which
contained only 11% of this acid. The Baltic green algae Enteromorpha
clathrata was characterised by a high amount of linolenic acid (16.7%),
whereas the red macroalgae from the Indian Ocean A. spicifera contained
large amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (13%) and oleic acid (11%).
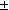 0.13
0.13 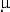 mol ml-1 to
25.337
mol ml-1 to
25.337 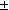 1.6
1.6 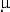 mol ml-1 during 32 h of anoxia.
High haemolymph lactate levels resulting from anoxia were associated with a
number of behavioural responses. The response of
R. harrisii tridentatus to very low levels of oxygen < 2 Torr
was relatively slow (LT 50= 24.3 h). Glycogen was found in
normoxic concentrations of 15.21
mol ml-1 during 32 h of anoxia.
High haemolymph lactate levels resulting from anoxia were associated with a
number of behavioural responses. The response of
R. harrisii tridentatus to very low levels of oxygen < 2 Torr
was relatively slow (LT 50= 24.3 h). Glycogen was found in
normoxic concentrations of 15.21 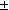 4.68
4.68 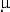 mol g-1 d.w.
These decreased after 6 h exposure to anoxia. The results are
discussed in relation to the metabolic requirements for
the survival of other crustaceans under low oxygen
conditions.
mol g-1 d.w.
These decreased after 6 h exposure to anoxia. The results are
discussed in relation to the metabolic requirements for
the survival of other crustaceans under low oxygen
conditions.